In this blog, we will be going to discuss what is industry 4.0, smart manufacturing, smart technology, four industry revolutions, and their amazing advantages.
Although the phrase “Industry 4.0” has been around for several years, the revolution itself is still fresh. Industry leaders coined the phrase “Industry 4.0” at the 2011 Hannover Messe, which is one of the biggest trade fairs in the world, held in Germany.
It talks about how automation and data analytics are currently experiencing a technological boom. Industry 4.0 is a term used to describe the significant change in industrial technology, which is known as the “fourth industrial revolution.”
Furthermore, it’s crucial to understand that when we discuss Industry 4.0, we are using a general term that does not specifically relate to any one type of technology. It includes all of the changes in the global industry that we are currently observing.
Cyber-physical systems, the Internet of Things, cloud computing, and cognitive computing are among the technological advancements responsible for the developments.
Now let’s get into a broader perspective and discuss Industry 4.0 in detail.
What is Industry 4.0?

The differentiating factor of Industry 4.0 is the innovative manner in which we integrate and connect these technologies. Transparent communication between systems enables integration and decision support. Moreover, it will take sophisticated, interconnected, and self-managing factories for technology to completely transform the industrial sector.
Industry 4.0’s major characteristics
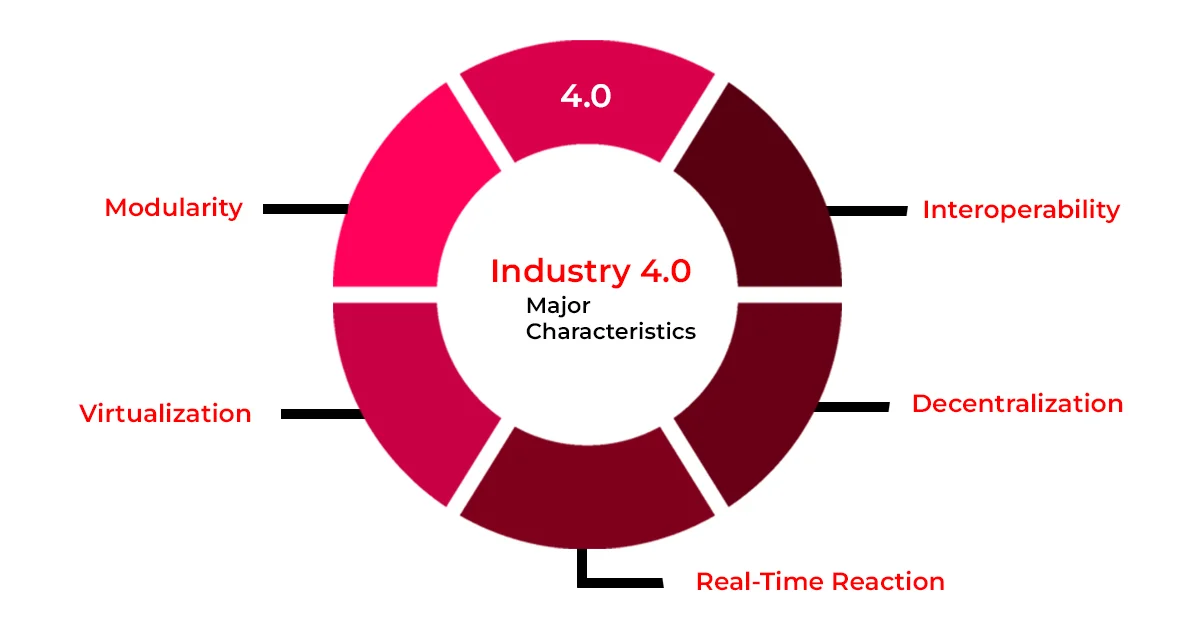
The integration of technologies to eliminate errors, speed up specific decisions, and save time is what makes this most recent industrial revolution unique. This enables the speedy and widespread expansion of digital production.
Similar features of the technologies which we will be discussing right now include interoperability, decentralization, and virtualization. Let us explain these features for your better understanding:
1) Interoperability:
It is a relatively contemporary terminology that refers to technical systems. In simple words, it is described as a system’s capacity to interact with or utilize the components of another system.
A straightforward demonstration of this is how every web browser can function with every web page because they both rely on open standards that everyone may access.
Although they do their own work, they both contribute to their achievement. The interoperability of physical systems, human systems, and computer systems is what defines the industry.
2) Decentralization:
It refers to spreading out duties and authority across a company, moving away from a single, major administrative center. An illustration of this is the shift to open-source software, which gives more individuals access to knowledge to encourage innovation and development.
Decentralization in Industry 4.0 refers to the absence of human intervention in the operation of machines. Physical systems have networked sensors that can make automatic decisions based on performance statistics.
3) Virtualization:
It is the process of making a virtual representation of something instead of a physical one. According to Open Source, the software gives the impression that they are running on a separate, dedicated machine, but its operating system, databases, and other programs are disconnected from the server.
Virtualized machines can be used to test various settings, run software tests, and check for updates before displaying the final product. These machines, on the other hand, are better protected against viruses. Additionally, without affecting the factory floor, you can create a virtual version of the smart factory for training and testing simulations.
4) Modularity:
It allows for quick changes to any production-line activity. Businesses can produce unique products sequentially by connecting and disconnecting various components without rearranging the entire assembly line.
Let us explain this with a clear picture. For example, the auto sector splits vehicle lines into modules to facilitate product assembly. Although the division is somewhat specialized, the production process can accommodate numerous colors, variants, and customer-specific requirements simultaneously.
5) Real-Time Reaction:
These are the new standards for the recent business world. This is due to the fact that technology has evolved so far that sensors now instantly send data to algorithms. With the support of this real-time data and analysis, problems may be addressed more quickly, and even preventative maintenance can be carried out.
Currently, several businesses employ this technology to offer comprehensive financial market information, including stock market quotations, economic indicators, and indexes.
Industry 4.0 Technology
As was discussed earlier, Industry 4.0 is the combination of various technologies for advanced industry automation rather than a single technology. The explanations of a few of these technologies are as follows:
1) Internet of Things (IoT) in Industry 4.0
Smart manufacturing relies heavily on the Internet of Things (IoT). The manufacturing floor’s equipment is outfitted with sensors that have an IP address, enabling the machines to communicate with other web-enabled devices.
Large volumes of valuable data can be gathered, analyzed, and shared thanks to this technology and connectivity.
2) Machine learning and AI
Manufacturing firms can fully benefit from the variety of data created not just on the factory floor but also across all of their business units, as well as from partners and outside sources, This is all possible due to AI and machine learning.
Moreover, Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are able to produce insights that give operations and business processes visibility, predictability, and automation.
3) Cloud computing
Cloud computing is a crucial element of any Industry 4.0 strategy. The connectivity and integration of engineering, supply chain, manufacturing, sales and distribution, and service are necessary for the full realization of smart manufacturing. The cloud makes that feasible for you.
Furthermore, cloud computing allows for more effective and efficient processing of the massive amounts of data that are saved and evaluated.
Additionally, for small- and medium-sized manufacturers who can appropriately assess their demands and scale as their firm grows, cloud computing can significantly lower startup costs.
4) Cybersecurity
The significance of cybersecurity or cyber-physical systems has not always been taken into account by manufacturing organizations. However, the same operational technology connectivity that makes industrial processes more effective also opens up new entry points for viruses and malicious attacks.
When experiencing a digital transformation to Industry 4.0, it is necessary to take into account a cybersecurity strategy that involves both IT and OT equipment.
5) Digital Twin
Digital twins, which are virtual clones of processes, production lines, factories, and supply networks, have been created by manufacturers thanks to Industry 4.0’s digital transformation.
To create a digital twin, data is gathered from IoT sensors, devices, PLCs, and other internet-connected devices. Digital twins on the other hand are a tool that manufacturers can employ to create new products, streamline workflows, and boost production.
Industry 4.0 Revolution
First industrial revolution
The first industrial revolution, which began in Britain in the late 18th century, made mass production possible by substituting water and steam power for just human and animal power. Instead of being delicately produced by hand, finished things were manufactured by machines.
Second industrial revolution
Assembly lines and the usage of gas, oil, and electricity were all introduced during the second industrial revolution, which occurred a century later. With the introduction of these new power sources and more sophisticated telephone and telegraph communications, manufacturing processes began to be automated and mass-produced.
Third industrial revolution
Now comes the third industrial revolution, which started in the middle of the 20th century. This industrial revolution improved production processes by incorporating computers, modern telecommunications, and data analysis.
Moreover, programmable logic controllers, which were used to automate some processes and gather and share data, were incorporated into machinery as the first step in the digitalization of industries.
Fourth industrial revolution
We are currently experiencing the fourth industrial revolution, commonly known as Industry 4.0. Informed data enables more efficient and productive manufacturing across the value chain, which is characterized by rising automation and the use of smart factories and machines.
In addition to that, increased flexibility enables factories to use mass customization to better satisfy client requests, eventually aiming to maximize efficiency.
Furthermore, a smart factory can improve decision-making and information transparency by gathering more data from the production floor and merging it with other company operational data.
Industry 4.0’s Advantages
The advantages of Industry 4.0 are already being felt by creative businesses. They saw early on how integrating new technology and investing in them could enhance productivity and profitability. Here are a few of the major advantages of Industry 4.0:
1) Enhanced Business Continuity
It requires maintenance when machinery, such as computers, malfunctions. Particularly in the field of information technology, this demands time, money, and team relocation. As a result, work is slowed down and output is impacted, which costs money and frustrates customers.
Problems can be tracked and foreseen if the machines are interconnected and under the control of the Internet of Things. Real-time proactive control is used to manage everything. The use of artificial intelligence algorithms enables more sophisticated and predictive system maintenance.
2) Boost productivity
One of the key objectives of Industry 4.0 is to boost productivity through automation and process optimization. This calls for decreasing expenses and losses, improving profitability, and speeding up production. Industry 4.0 provides fewer interruptions to production while also focusing on the upgrading of the production line.
3) Personalization
The modern consumer has altered in terms of behavior and tastes. Technology simultaneously changed the way we work, shop, interact, and live. In today’s digital era, customers have higher expectations, so we must personalize our offerings to satisfy them.
Personalization enables customers to communicate directly with the business in addition to receiving exactly what they desire. It is essential to encourage better client experiences. Therefore, businesses that wish to scale their personalization services and achieve a competitive edge must realize and apply Industry 4.0 concepts.
4) Responsiveness
The main advantages of Industry 4.0 are adaptability, scalability, and responsiveness. The industry is increasingly adopting many of the same techniques that IT uses to scale swiftly.
Robotics, big data, cybernetic systems, and artificial intelligence are necessary to meet and predict seasonal demand and supply changes. These innovations enable organizations to remain adaptable and even foresee future developments.
5) Improved Working Environment
Essential goals for business include enhancing working conditions and enabling workers to engage in less stressful professions. Drones, robotics, wearable for workers, proximity sensors for cars, and smart PPE are just a few of the new digital tools which improve employee safety.
These are capable of undertaking dangerous work, completely replacing people, or in the case of some wearable, supporting people who are conducting physical labor, such as carrying heavy objects.
Additionally, modern digital manufacturing technologies let you quickly find and pinpoint flaws to improve accident prevention.
The influence of Industry 4.0

Every industry will be influenced by the developments in the fourth revolution. Every aspect of the business is affected, just like in earlier revolutions.
IoT and connected devices will have a noticeable impact on Industry 4.0. According to Research, from 13.4 billion in 2015, there will be 38.5 billion linked devices by 2020. That’s a rise of more than 285 percent!
Additionally, one more example of how digital technologies may help production management is in the area of asset maintenance, where it can be used to improve operational capacity and planning. The capacity to monitor equipment to spot issues beforehand has already been recognized as a crucial element.
Future working dynamics
The workforce will be one of Industry 4.0’s most important impacts. According to a report from 2018, the number of industrial robots has increased by 17% a year since 2010. However, just five nations account for the majority of that growth.
All these technical advancements eventually create some difficulty or stress, as this has happened before throughout past industrial revolutions. Automation is viewed as a risk to employees by many professionals. However, a lot of business leaders think that automation might create jobs.
In the same study, it was discovered that half of the executives suspect that automation promotes innovation since it provides more flexibility for individuals to pursue the work they want to accomplish.
Moreover, research by the Boston Consulting Group indicates that by 2025, there would be 6% more jobs in Germany, which lends support to this concept. According to the theory, the demand for technological jobs is growing faster than the loss of operational jobs.
According to another research, 65% of elementary school-age students will hold jobs that don’t yet exist. These new occupations will probably be in the fields of data analysis, robotics, programming, engineering, math, and the mobile and internet industries. Critical thinking on the other hand is this career’s primary characteristic.
According to predictions by studying all such research for the labor market, businesses and professionals must innovate and change in order to survive. Future job criteria ultimately will emphasize training, innovation, courage, and the capacity for teamwork.
Industry 4.0’s obstacles

In many industrial and commercial sectors, the adoption of Industry 4.0 will result in major adjustments. Therefore, throughout this period of transition, we must be aware of the difficulties and how to overcome them.
1) Limited Knowledge
Most businesses are having trouble filling positions requiring specialized skills because the workforce of the future will require new knowledge and skills. That is why development is being delayed and organizations are becoming less competitive as a result of a lack of training.
On the other hand, workforce training is becoming more popular in the US to professionally train workers. And larger-scale implementation of these initiatives is necessary for regional success. However, you have to keep in mind that the annual cost of such initiatives might be costly.
Additionally, it is important for managers and decision-makers to think creatively. Industry 4.0 has the potential to provide businesses with new business models, but design thinking principles must be used properly.
2) Low Safety and Security
Security is certainly one of the big obstacles in Industry 4.0. It is not easy to integrate a large volume of data into various systems via a computer network. There are new threats to your network due to cloud computing and newly linked devices. Furthermore, it is said that there is a greater potential for risk as information access increases.
One of the major priorities for the I.T. sector is keeping information away from malicious hackers. Therefore, to counter such activities, new systems and technologies are available that will monitor problems and avoid them, assuring the security and safety of data transfer.
3) Implementation Cost is High
One of the major obstacles to the Industry 4.0 is the high cost of technology implementation. Newer technologies are still pricey even though the cost of robots is declining. Hence, it will take some time for these technologies to become more accessible and cost-effective. However, you’ll already be falling behind your rivals in terms of digital innovation by that point.
Working with outsourcing service partners can be a solution to this issue. Recognizing their lack of IT expertise, manufacturers look to outsource services to execute the best solutions. They may save money and advance economically as a result of this.
The American Industry 4.0 Market
In terms of production, the United States ranks second globally. However, it has experienced sharp decreases since the time of the revolution. China surpassed the United States to become the world’s largest manufacturer in 2010, according to estimates from the U.N.
Still, some companies are spending a lot of money on Industry 4.0. According to studies, American firms, with the exception of those in China, spend significantly more on research. The truth is that manufacturers have been responsible for roughly 68% of all R&D undertaken by corporations in the United States in recent years.
According to research, American tech tycoons are dominating the Industry 4.0 sector. By enhancing and integrating supply, manufacturing, maintenance, delivery, and customer support, they are investing billions in business solutions.
However, that doesn’t necessarily indicate that these solutions are entering full-scale production. According to a McKinsey report, international businesses are testing an average of eight different Industry 4.0 technologies. The United States, at 8.5, is slightly over average but well below China’s 10.2. However, only 30% of those pilots are implemented company-wide globally.
Future opportunities are limitless. If the correct investments are made, the competitive edge the United States currently has in a few sectors might improve manufacturing value. Computer electronics, automobiles, and aerospace are just a few of the sectors.
Upcoming Trends in Industry 4.0

You may expect that software, platforms, and apps will play a larger role in technology in the years to come. By utilizing simulations, digital automation, 3D mini-printers, and other technologies, these solutions seek to advance Industry 4.0. Some of the most popular technological trends are listed below:
3D Printing
Technology for 3D printing is developing rapidly, and it is becoming more and more popular. Many businesses are already considering innovative technological solutions, largely to cut the price of manufacturing new models or repairing broken ones.
Besides manufacturing, 3D printing has a broad impact. Universities, for instance, can create models for learning using 3D printers in the educational sector. Students are learning new technology while also gaining digital skills through this.
Cobots
Many businesses believe that rather than being entirely automated, factories of the future will be more collaborative. In this context, the term “cobot” refers to robots that collaborate with humans while performing manual activities.
As opposed to industrial robots, which automate everything, this technology requires a far lesser investment. Cobots, on the other hand, make movements that are both precise and agile like a robot and sensitive and flexible like those of a human.
Integration
The fourth industrial revolution’s guiding principles are integrating, linking, and cooperating. Adding sensors to every machine won’t be enough to collect all the data. Instead, you must understand how to effectively employ sensors. Applications, software, and IoT platforms all need to be connected for integrated automation to work.
Conclusion
We hope now you have got a clear idea about what is Industry 4.0, smart manufacturing, and smart automation.
Industry 4.0 is basically changing the way production is done by introducing new concepts, insights, and technologies that are freely available due to digital solutions that are meant to improve industrial productivity.
Modern manufacturers will rely on tools that can make proactive, fact-based decisions through automation and big data analytics. The future of manufacturing will also feature high-volume and customized production along with improved client engagement and behavior patterns.
Eventually, smart manufacturing will rely on fast, innovative processes to keep up with the speed of technology. Companies will be more prepared to flourish in the digital future if they learn, adapt, and put Industry 4.0 techniques into practice.



