In this blog, you will get to know the true meaning of business process management, its benefits, lifecycle, examples of BPM, and its types & technologies.
Let’s begin with Business Process Management Definition. BPM is a technique in which a business takes a look back and examines each of the processes both collectively and individually. It investigates the situation in its present form and points out possibilities for development in order to build a more effective and efficient workplace.
A business process on the other hand is an action or series of actions that contribute to achieving a company’s objectives, such as boosting revenues or encouraging diversity in the workforce.
What is Business Process Management?

BPM employs a variety of techniques to enhance a business process, including analysis, modeling, how it functions in various circumstances, adjustments, monitoring, and continual improvement of the new process’s capacity to produce desired business objectives and results.
The organizational roles, guidelines, strategies, business objectives, and other components that BPM incorporates are always evolving, making it a vast and versatile subject by definition. Agile, Six Sigma, lean management, and other optimization approaches have all been supported by BPM over the years.
BPM software packages were created to enable significant business development as business processes at some firms were too massive and complicated to be handled without the assistance of automated tools.
As AI, machine learning, and other known intelligent technologies grow, these enabling BPM technologies have also advanced, offering new methods for discovering, designing, measuring, improving, and automating workflows.
With the growth of digital business, the traditional focus of BPM on back-end processes has now shifted to the optimization of customer and employee engagement systems.
Starting Business Process Management
Business process management can be a difficult subject to understand. Based on an organization’s size, process maturity, level of technical skill, organizational values, and resources, its practice differs greatly.
The implementation of BPM’s ideas and practices might range from managing a single process, like adding a new client, to managing a significant corporate transformation requiring the integration of entirely new procedures.
The ability of a business to recognize the value of process improvement plays a significant role in the success of a BPM project. This thorough BPM guide describes what exactly Business Process Management is, its benefits, the difficulties it presents, and best practices for using it successfully in order to help big and small businesses get more out of their business processes.
Additionally, you’ll find projects that demonstrate business process automation and process optimization, a summary of the most recent BPM tools, the overall cost of BPM, and some key factors to remember before buying BPM software.
Amount of Concerns in Business Process Management
The enterprise level, business process level, and implementation or resource level are the three different “amounts of concern” that Harmon distinguished between in his book Business Process Change.”
The supply chain management process of a corporation was the focus of a BPM project, as demonstrated by Harmon. An enterprise-level BPM team may conclude that the company’s supply chain is not running well and start the project by redesigning the process.
After conducting research, the redesign team makes recommendations that need to be approved by top management. In this scenario, the redesign entails the purchase of a fresh ERP system, involving the IT division. Also Involving HR, as it generates new job responsibilities that demand training programs.
Business Process Management Challenges
Any corporate venture that entails reshaping the established order is full of challenges. This is particularly true with BPM, where the difficult challenge of process improvement involves numerous roles, systems, and methods of operation.
According to a report by technology journalist George Lawton, who covers technology-enabled business transformation, businesses must be ready for whatever issues they may face and have a strategy for dealing with them in order to get the most from BPM.
According to Lawton, the following challenges are the main causes of BPM failures:
- Undefined business proposes and goals
- Insufficient accountability and visibility of the process
- Rigid contracts and rewards with third parties.
- Limited testing facilities
What are the BPM lifecycle stages?
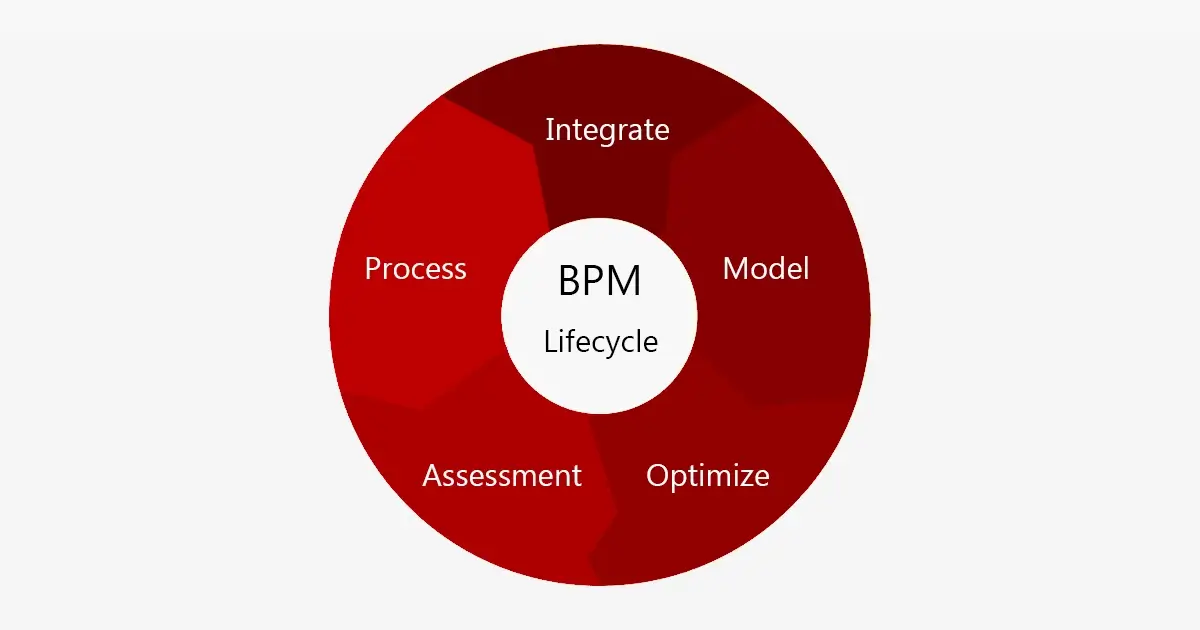
The stages of a workflow are first defined by a productive BPM system. The team can use these indicators to track their success and find areas for improvement. Businesses can improve their operations and provide better financial results by implementing business process management.
You need to have a thorough understanding of the BPM lifecycle to accomplish these objectives. Following are the five stages of the lifecycle you should be aware of:
Process
The process milestones should be defined by the team first. The task owners for each step in the workflow should then be identified together with specific tasks inside the larger BPM process. The processes should be precisely described so that the team can decide which areas to improve the process in and which metrics to use to measure its progress.
Model
This step requires the team to illustrate the process model visually. This should contain precise information, such as timeframes, job descriptions, and any data flow during the process. Software for business process management can be very useful at this point.
Integrate
The panel should test the new BPM system with a small group as part of a proof of concept. Then the panel can start introducing the procedure to a larger audience after taking any input into account.
Assessment
The panel should keep an eye on the procedure during this stage, assessing productivity improvements and spotting any new obstacles.
Optimize
At the final stage, the panel makes the necessary changes to the business process to improve efficiency.
Business process reengineering, or BPR, is a sixth stage that some professionals include to describe what happens when changes to an existing process no longer achieve the desired business objectives and require radical reinvention, typically incorporating the extensive use of automation.
The BPM lifecycle appears to be simple enough, yet each stage might take weeks or even months and demands proper management. Business operations frequently involve several departments and systems.
For instance, the process of onboarding a new employee may engage not just HR but also the IT sector for the issuance of computer equipment and security credentials, finance for the preparation of tax paperwork, boot camps for on-the-job training, and so forth.
Additionally, the work of exploring and analyzing existing workflows, developing and trying out new models, and optimizing a business process can yield hundreds of documents. Hence, if BPM is not properly handled, there is a lot of possibility for failure.
Types of Business Process Management
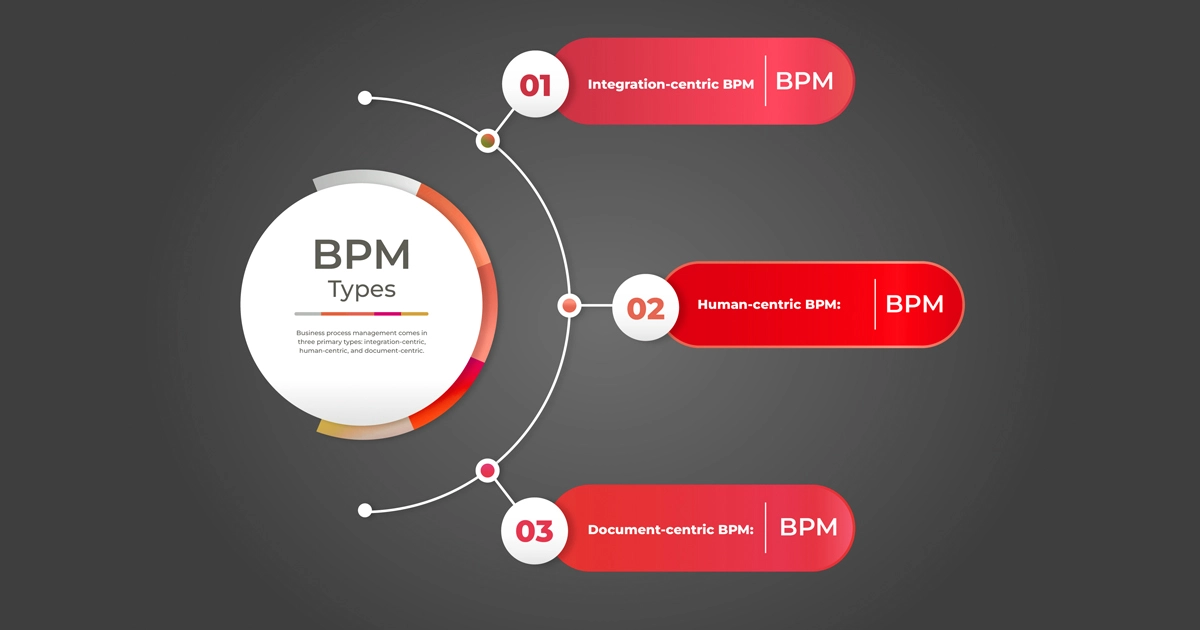
Business process management comes in three primary types: integration-centric, human-centric, and document-centric.
Integration-centric BPM
This kind of BPM concentrates on operations that don’t entail a lot of human interaction. These procedures rely more on APIs and technologies that link data from other systems, such as customer relationship management (CRM) and human resource management (HRM).
Human-centric BPM:
This sort of BPM, in contrast to integration-centric BPM, is focused on human interaction, usually when permissions are necessary. Teams can assign tasks to various roles using drag-and-drop features in intuitive user interfaces, making it simpler to hold people accountable throughout the procedure.
Document-centric BPM:
This kind of BPM is mainly focused on a particular document, such as a contract. To create a contract between the client and vendor, businesses must go through a number of documents and approval processes before making a transaction.
Benefits of Business Process Management

A number of benefits are produced by BPM systems, which raise organizational value through process improvement. The following are some of them:
1) Better Experiences For Both Employees And Customers
BPM software helps to reduce repetitious tasks and improve information accessibility. Distractions are eliminated so that staff can concentrate on their work and their clients, which promotes client satisfaction. The learning curve during the employee onboarding process is also shortened by clear workflows, increasing productivity and engagement.
2) BPM helps in improving efficiency and reducing costs
BPM solutions help in both the improvement of already-existing processes and the addition of a greater framework during the creation of new processes. This is accomplished by removing barriers and unnecessary steps in the process, which boosts efficiency. Moreover, businesses that are more agile can accomplish their goals more quickly and divert any extra resources to projects that are of the greatest propriety.
3) Increases Transparency & Reduce Dependence on Development Teams
Business process automation increases accountability and transparency throughout a particular process by clearly defining owners for each task along the way. As a result, team collaboration is also increased.
On the other hand, BPM provides low-code features that eliminate potential reliance on development. With these technologies, business users may be onboarded fast and easily, enhancing process automation throughout the organization.
4) BPM Enhances More Flexible Process
BPM makes it possible for greater workflow automation and process execution, which applies well when expanding processes to different regions of the globe. Solutions for business process management specify responsibilities and ensure consistency across the process. They can also highlight opportunities for business rules to be incorporated for automation, enabling teams to concentrate more on creativity.
Business Process Management Examples
Solutions for BPM are implemented by various organizational departments. The following are some examples of how it is applied to accomplish corporate goals:
Customer support
When a team is overloaded with customer calls, staff in customer service might identify commonly asked queries for chatbots to answer. In order to better automate procedures and provide clients with more personalized responses, transcript data from call centers and chatbots can also be useful.
Human resources
BPM can be used by HR to optimize workflow and documentation. It offers a more structured framework for processing HR forms, including those for hiring and firing employees, performance reviews, leave requests, and timesheet approval.
Finance
Businesses can build templates to standardize the filing of purchase orders from different teams, enabling them to acquire company software or hardware more swiftly. Additionally, for particular instances, customized workflows can be built.
Content distribution
BPM can be used by media companies to automate the creation, distribution, and maintenance of content. Systems for content management, rights management, content flow, and work orders can all be integrated with business process management software.
Order fulfillment
With the help of BPM, businesses can increase the operational effectiveness of their order fulfillment systems. They can control special offers, order capture, and order fulfillment using BPM. As a result, the procedure is changed to focus on customer-centric order management, which generates more company value.
Banking
Banks must assess applicants for potential credit risk when processing loans for individuals or companies. This entails gathering data from several sources, including applicants, employers, and credit rating organizations. Business Process Management simplifies the decision-making process for loan eligibility by controlling the information flow throughout the procedure and minimizing documentation errors.
Why Business Process Management?
Effective business processes are essential to the success of an organization, which is why business process management is necessary. The following are some illustrations of processes that assist businesses in achieving their business objectives:
- Executing a Product Order
- Incorporating a new hire
- Administering customer care
These tasks are broken down into defined, repeatable phases by a well-designed business process so that employees can follow them and deliver favorable results. Organizations may estimate their resource needs thanks to repetitive actions, which reduces the possibility of under or over-allocating resources. Measuring the steps identifies problem areas and obstacles, pointing to areas where business processes should be improved.
Additionally, these corporate procedures can involve hundreds or even thousands of activities and approvals. Business process outsourcing companies may also be involved, as they frequently involve employees, IT systems, and other technology within the company.
On the other hand, a business can suffer from a badly designed or managed business process that limits productivity and efficiency. A process that is ineffective can actually be made worse by automation, which will damage company objectives.
To prevent this, business process management (BPM) employs systematic techniques for identifying, analyzing, enhancing, automating, and continually monitoring business processes. When used effectively, BPM aligns processes with organizational objectives and supports businesses in providing goods and services more cheaply and efficiently.
As per the process experts, another reason for the BPM approach’s continued real significance is the way it helps businesses adapt to changing needs.
Business Process Management Technologies

Business process management technology combines BPM tools, solutions, and methodologies to enable efficient business process modeling, significant process transformation, and thorough BPM process management.
By automating, managing, and optimizing business processes, BPM technology facilitates organizations in achieving flexibility, transparency, and efficiency. The four essential aspects of BPM technology are as follows:
Designing processes
In order to accomplish the desired business outcome, this refers to creating, visualizing, and modeling a business process or workflow at the beginning of business process management.
Deployment of Applications
This is the point at which automation technology is applied to accomplish configuration, information management, and the creation of an end-user task list for more smooth business process transformation.
Evaluating Performance
To continuously enhance corporate processes for increased efficiency, management technologies including project management dashboards, reporting tools, and analytics are implemented at this point.
Enterprise Application Integration
This term refers to the tactical integration of BPM tools, frameworks, and technological solutions with legacy systems to avoid any disruption associated with system and process upgrades while maintaining the full operational capability of all business functions and services.
The intelligence, innovation, and simplicity that BPM technology offers business users set it apart from other technologies. In order to achieve process excellence and stay ahead of the curve, businesses have a great opportunity to take advantage of the tremendous spread of technology by implementing the newest tools and technologies.
A successful business plan on the other hand uses the most up-to-date technology to constantly enhance and automate business operations to ensure that corporate objectives are always achieved.
BPM technology typically demonstrates its full value when it converts information and analytics into useful business insights. Businesses can accomplish this by implementing an artificial intelligence platform or solution that can quickly and accurately gather, preserve, and audit massive volumes of data.
The ultimate outcome is business process automation and workflow management which is more advanced.
BPM Technology Examples
1) Rules Engines
An organization must specify how a defined business process will be carried out. This also applies to the tasks that are a part of every process and workflow. Because of this, it’s critical to create and uphold a precise set of business standards for management processes, including decision-making guidelines, operational guidelines, legal and regulatory guidelines, etc.
The development, documentation, and efficiency of business process rules are supported by rules engines. They provide a pathway for business process improvement and standardize the management of that process.
Process analysts can utilize rules engines to test, update, and create new business rules, as well as to carry out version control and approval procedures are implemented after a business process description and a defined rulebook are in place.
2) Process and Workflow Modelers
The analysis of business processes and the creation of thorough documentation of the opportunities, risks, volume results, and obstacles they contain are made possible by modeling tools. An organization can use this technology to determine the actions, duties, and responsibilities that make up each business process by drawing a flowchart of it.
In order to map out prospective modifications, process analysts can then collaborate to update these diagrams on a single platform. The end result is the creation of a brand-new, improved version of the process that already includes the enhancements. The process must then be executed and automated by the company.
3) Business Process Monitoring
A comprehensive, in-depth view of the management and execution of business processes is provided by this technology. As obstacles and problems arise, process analysts can make decisions and take immediate corrective action using data and analytics. As a result, the performance of businesses is subsequently more optimized.
The most popular application of this technology is management dashboards, which make use of graphic components like graphs, tables, and listings to give a thorough overview of a whole procedure. To fully understand the scope and potential of their operations, businesses need this visual information. A business, on the other hand, may better manage and enhance all of its processes with such type of visibility.
4) Business Process Management Suites
A comprehensive technology environment known as a BPM suite allows organizations to model, carry out, optimize, monitor, and automate business processes all from one location. It creates all the solutions a company needs to implement business process management by integrating cutting-edge BPM software. It would not be wrong to say that it’s like a complete package of BPM technology.
List of BPM Vendors
BPM tools are available in an ever-increasing variety. Advanced solutions have all been included in conventional BPM companies’ platforms recently. Moreover, several of the major corporate software providers have increased their BPMS capabilities through acquisitions or new product development.
Hence below are a few of the reliable vendors which we have searched for you:
- IBM
- BP Logix Appian
- Pegasystems
- Trisotech
- Tibco Software
- Appian
- Microsoft
- Kissflow
- Jira
- SAP Signavio
Business Process Automation V.S Business Process Management
Business process management (BPM) and business process automation (BPA) are similar and even compatible in some aspects, but they are not the same. Process automation is the focus of BPA, whereas process management, which may or may not include automation, is the focus of BPM. In short, not every BPM may involve BPA, but all BPA can be thought of as a sort of BPM.
Any practice used to automate and optimize corporate processes is referred to as business process automation (BPA). It can adopt a vast range of apps and solutions that seek to increase performance, adaptability, efficiency, and accountability in regular business tasks.
On the other side, BPM is an organized strategy for enhancing business operations. Everyone will have a greater understanding of how they contribute to the accomplishment of company goals when it is successfully implemented. This usually results in a stress-free, more effective workforce, which usually leads to satisfied clients, higher profits, and fewer expenses.
Business Process Management Overall Cost
The cost of a BPM project, according to specialists like Morris, varies greatly based on the project’s scale, the number of users, the number of transactions that will be processed per hour, the number of locations that will access the applications, and the annual utilization and etc.
Project managers must investigate which BPMS features are essential and which would be nice to have but not necessary once they have determined how the organization intends to use BPMS going forward.
Data storage, cloud utilization, and fees for technology training are all related to processing expenses in addition to vendor pricing. A BPM suite could cost as little as $50,000 per year to improve a single process all the way up to $1 million per year for a big firm employing BPMS for numerous processes or in numerous products.
Factors to Consider when buying BPM Software

There are certain factors that you need to consider before buying business process management software for your organization. Hence, we recommend you focus on some key factors which are mentioned below:
Goal
Your goal is the key consideration and stepping stone to the best BPM system. You should be asking yourself what process-related goal or issue you are attempting to resolve.
The numerous types of BPM software that are out there are used for various tasks. While large corporations may require a complex system that may require departments to connect with other software, however, on the other hand, small firms may only need simple process automation with a basic interface. That’s why it is said to always specify your goals.
Pricing factor
Ultimately, it all comes down to how much money you’re prepared to pay and how much it’s worth. It has a significant impact on your choice. Therefore, examine the offerings at various price points. You should check which is most appropriate according to your organization`s goal.
Execution Time
Businesses must inquire in advance about the timetables for execution because time is a crucial asset for any organization. Business owners should ask their BPM service providers how long the project will take, from signing the required documents to actually using the software.
User friendly
Businesses frequently create highly effective systems, but most of the time they are so complicated that the employees are unable to use or even grasp them. Therefore, always check that BPM software is user-friendly before choosing it. You can offer trials to some employees so they can test them out and provide opinions.
Secure
Security is sometimes ignored by businesses as a key consideration when assessing their BPM software. However, please be sure that security is of the biggest significance when choosing BPM software.
Commencing with the platform itself, moving on to the platform’s hosting cloud infrastructure, and finishing with the ready-to-use applications built on the platform, all of these essential components must comply with the strictest security requirements.
Conclusion
Business process management (BPM) is an organized approach to improving the efficiency and effectiveness of business processes. It involves the identification, analysis, and improvement of business processes to achieve specific objectives such as reducing costs, increasing revenues, or improving customer satisfaction.
Furthermore, BPM is a continuous cycle of activities that begins with the identification of process improvements and ends with the implementation of those improvements. Eventually, if you’re looking to improve your business processes, then consider using a BPM approach. It can help you identify areas for improvement, implement changes, and track the results to ensure that your efforts are paying off.
FAQ
How do I know if my business needs Business Process Management?
If your organization deals with multiple departments and teams, you probably have multiple systems in place. Maybe some of these systems integrate, but some do not, resulting in duplicate data and disturbing internal communication, which causes interference in daily business operations, and prevents you from taking advantage of your most valuable resource, your team.
If you face such scenarios then you definitely need BPM. This is just one basic example. There are many others that we have discussed in this blog.
Why should I Implement Business Process Management in my organization?
Business Process Management (BPM) brings structure to a business and makes it easier to manage. BPM enables companies to create and execute business processes, which automate company policies and workflows. Essentially, BPM makes an organization more productive that generates positive outcomes.
Why is BPM significant for my team?
The following list of factors will help you understand why BPM is significant for your staff:
- Reduces employee burdens and eliminates the tasks that don’t provide value
- Makes the staff and processes more productive
- Improves process cycle time
- Improves teamwork and enhances internal communication between groups and departments


